KYC — meaning 'know your customer', or 'know your client' — is a critical function for any organization where private information is at stake. Businesses employ the KYC process to establish their customers’ identities and assess and monitor any associated risks on an ongoing basis.
Put simply, businesses need to perform KYC compliance to ensure a customer really is who they say they are. With more and more interactions taking place in a digital scenario, verifying the identities of your online customers is crucial. Confidence in your customers’ identities provides a solid basis on which to conduct further due diligence and customer risk assessments.
In addition to initially verifying your customers, KYC requires constant monitoring and possibly updating your risk assessments. For businesses, a KYC update means anything from implementing verification software that better keeps up with fraud techniques, to adjusting your compliance so they match with new regulations.
Is KYC only mandatory for crypto or finance?
While KYC often finds use in financial services, it is not strictly for the financial industry. KYC has applications in real estate, telecommunications, and other industries. Oftentimes, KYC is a mandatory legal requirement for organizations. The specific KYC requirements will vary from industry to industry, as well as from country to country. This means that two banks in different nations may have completely different KYC requirements.
The goal of KYC checks within financial services is to prevent or limit money laundering, terrorist financing, corruption, and other illegal activities. For example, The United States defines KYC requirements in the Patriot Act by outlining two concepts: Customer Identification Programs (CIP), and Customer Due Diligence (CDD).
While other industries might not have to do KYC by law, there are other reasons they might consider it. Regulations are tightening around the world, and as more interactions move online, knowing your customer is becoming increasingly important. The range of businesses that need and want to carry out KYC checks is widening — particularly in burgeoning financial services spaces such as cryptocurrency. Whether you’re in financial services or simply a customer-centric industry, developing a ‘know your customer’ checklist ensures a high level of customer service and data protection.
Why is performing KYC important?
KYC verification — meaning the process of fully ratifying a customer’s identity and risk level — is critical for three reasons: meeting compliance requirements, building trust, and preventing fraud.
1. Meeting compliance requirements
Know Your Customer (KYC) procedures help prevent financial crime and money laundering. For financial institutions, it’s a legal requirement to verify the identity of their customers in compliance with laws and regulations. This includes Anti-Money Laundering (AML) laws.
KYC requirements differ by geography, so it’s important to check local regulations. In Europe, the two most relevant pieces of legislation for KYC are the GDPR and the AML5 directive (or 5AMLD). Businesses will also want to familiarize themselves with eIDAS regulations.
However individual countries can also impose their own additional requirements. In Germany, institutions must implement video KYC processes as part of their customer identity verification. Spain requires enhanced liveness detection, France a secondary identity document, and Italy seven additional risk checks.
In the US, the Financial Crimes Enforcement Network (FinCEN) is the main AML regulator. The Bank Secrecy Act (BSA) is the most important anti-money laundering law. The USA Patriot Act targets financial crimes associated with terrorism. The US is also a member of the Financial Action Task Force (FATF).
Failure to comply with KYC/AML laws and regulations can have serious consequences. The most serious violations can result in fines and imprisonment. Lax anti-money laundering and KYC compliance are some of the most common issues that result in fines. One example includes Westpac Bank (Australia) who were fined $900 million for AML breaches.
2. Building trust
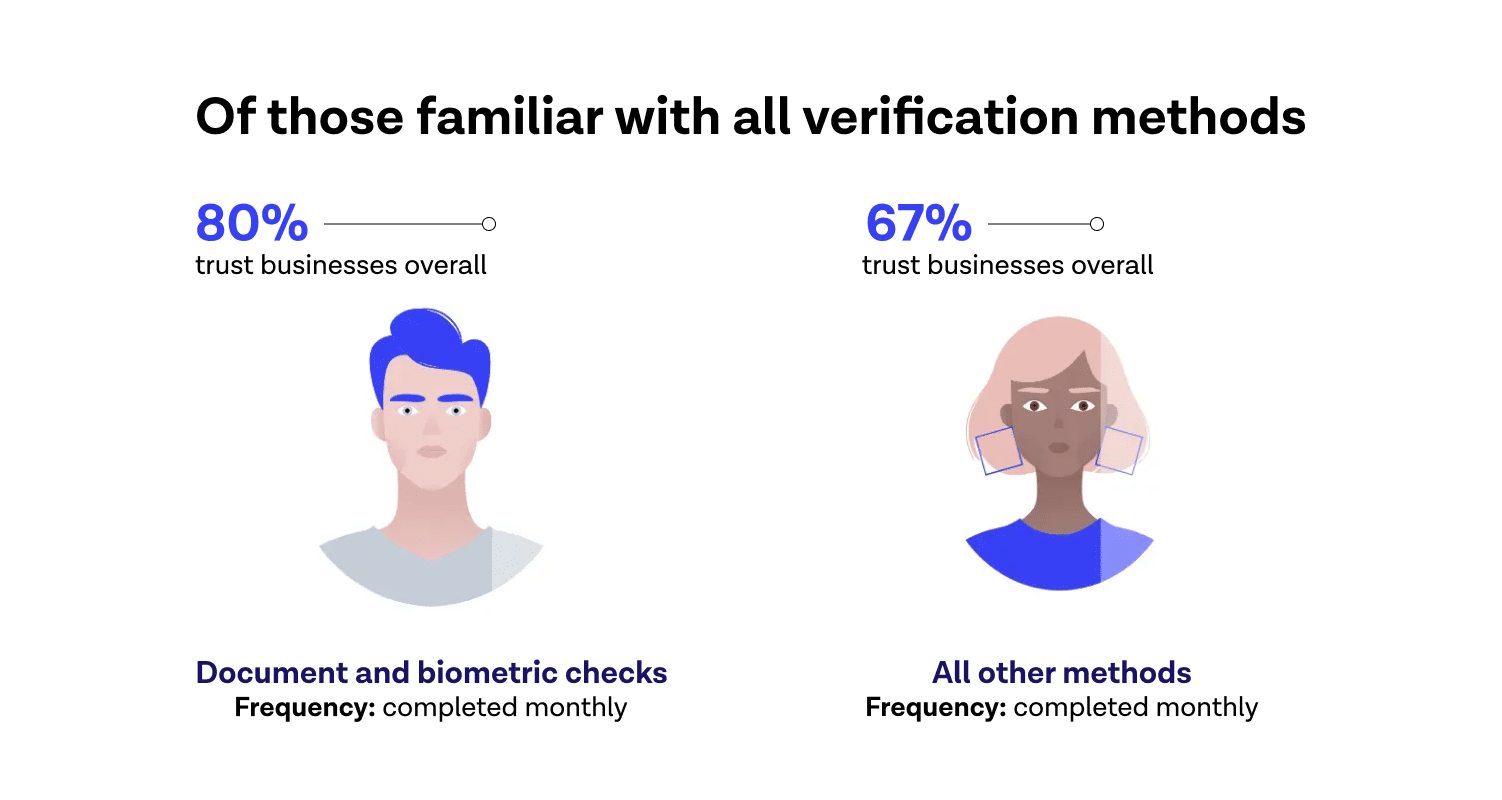
Not all industries are legally required to perform KYC checks. But for some, KYC is important in business because it helps an organization build trusting relationships with partners. More of our interactions are taking place online, KYC practices are especially relevant. They’re usually the first step in a customer relationship with a company. In fact, a secure identity verification check increases trust in a business. 80% of users trust businesses overall when they use document and biometric checks as part of this process.
And this trust doesn’t just apply to business-customer relationships. It also applies in peer-to-peer environments, such as marketplaces or sharing communities. Customers want to know that peers they’re buying from, or drivers they’re sharing a car with, have been vetted. It’s clear, then, that one of the core benefits of KYC is an improved customer experience — which then increases customer trust.
Failing to meet customer expectations when it comes to trust can have detrimental consequences, from a reputational standpoint to losing your customers to competitors.
3. Preventing fraud
It’s obvious that fraud has a financial impact. In fact, it costs the global economy $5 trillion a year. And our own research shows that fraud is increasing, in both quantity and quality of attacks. In our Identity Fraud Report we saw attempted fraud in financial services surge 23% in 2022.
But, traditional approaches to preventing fraud are no longer enough. Due to large-scale data breaches, huge amounts of personal customer data are now available to buy on the dark web.
This is where a robust identity verification approach as part of KYC comes in. It’s no longer enough to simply rely on database checks alone for verification. Better KYC practices can help defend against bad actors who exploit weak methods of verification.
What is KYC verification?
The KYC process steps typically use the following three components.
- A customer identification program (CIP)
- Customer due diligence (CDD)
- Continuous or ongoing monitoring
Customer identification programs (CIP) collect information (such as name, date of birth, and address) during the onboarding process or account creation. As part of this, organizations need to verify the identity of customers within a reasonable timeframe.
This verification process can include identity document (ID) verification, face-to-face or in-person verification, address verification (eg. utility bills), biometric verification, or any combination of these.
Organizations set KYC policies based on the risk-based assessment strategy. Account type, services offered, and customers’ geographic location among other things are usually considered.
Customer due diligence (CDD) is a key component in establishing trust between your business and your customer. Depending on the risks involved in the relationship, there are different levels of customer due diligence.
Simplified due diligence applies where the risk of fraud or other illegal activities is considered low. Basic CDD is the standard approach. Enhanced due diligence comes into play in higher-risk situations.
Learn more about the differences between CDD and EDD in this article: What’s the difference between CDD and EDD?
Some examples of CDD steps include:
- Gaining an overview of a customer’s business activities
- Determining the potential risks associated with the customer, for example politically exposed persons (PEPs) and sanctions screening
- Performing periodic assessments to determine if the existing risk category is still applicable
Continuous or ongoing monitoring applies when an initial check is not enough to establish long-term trust and to check whether a customer's situation changes. Situations that might call for ongoing monitoring include: unusual account activity (e.g., spikes), upticks in fraud or illegal undertakings, and the inclusion of the customer on sanction lists. The level of monitoring generally depends on the risk-based assessment and strategy.
What is required for KYC verification?
The specifics of KYC will vary depending on your institution and location. If we take financial services as an example, someone who wants to open a bank account may be required to provide a collection of KYC documents, meaning any official items that prove their identity and their address. This may include a form of government-issued identification, such as a driver’s license, passport, or residence permit. Different institutions may ask for different KYC documents depending on their requirements, and certain customers may be required to provide more information depending on their assessed risk level. Additionally, institutions in different countries may require different forms of verification.
How to do KYC verification using digital solutions
As part of Customer Identification Programs (CIP) businesses need to take measures to verify the identity of their customers — in other words, have reasonable assurance that their customers are who they say they are.
This identity verification step usually happens at account opening, or within a reasonable time of the account creation. It can happen both remotely and in person. When done digitally or as part of online KYC checks, it’s referred to as eKYC (electronic Know Your Customer).
A secure digital identity verification usually involves a mixture, or all, of the following:
- Document/ID verification: checking that an ID is valid and genuine
- Biometric verification: comparing facial biometrics with a photo ID document, to confirm the person is submitting their rightfully owned document
- ID record validation: validating customer data against trusted databases
Watchlist screening and ongoing monitoring: checking customer-provided data against relevant sanctions, PEPs, and adverse media databases
Our compliance manager’s guide to identity verification summarizes the global regulatory landscape, best practices for building customer identity programs, and what to look for when choosing an identity partner.
The above approach to identity verification allows businesses to anchor customers’ digital identities to their real selves. It helps businesses offer a smooth customer onboarding experience that complies with KYC regulations and reduces the risk of fraud. The information captured at this stage also has application when conducting further due diligence, risk assessments and ongoing monitoring.
As a result of the pandemic in 2020, many companies have shifted to an entirely digital KYC approach. But adopting digital identity verification as part of an eKYC solution offers several benefits in its own right.
Customer onboarding speed
In a Thomson Reuters survey, 30% of respondents stated it takes them over two months to onboard a new client. 10% indicate it takes over four months. This isn’t the best first impression to leave with your customer. Some customers will even abandon the process (up to 43%), which in turn hurts revenue growth. A more efficient eKYC and identity verification solution can turn this around and complete the onboarding process in a fraction of the time.
Improved customer experience
KYC provides an experience that is not only quicker, but better overall for customers. A mobile or internet-first approach makes life easier for your customers. Our customer KOHO reduced their time to verify a new user by 98%, and increased onboarding conversion by 15%.
Accuracy
To determine the validity of a large range of document types, you can’t rely on humans alone. Mistakes, such as those made by human error, can slow down the process and add extra costs. By automating many of these processes, you can avoid errors and have more time to fix any mistakes.
Automation
Part of KYC checks will usually involve assessing an identity document to ensure it’s genuine. In an online environment, this becomes extremely challenging. Identity documents are complex — and there are hundreds of thousands in circulation, from different countries. Using a software solution specifically designed for KYC processes, such as biometric verification, cuts down on a lot of time (and money) spent while also improving efficiency.
Cost
Digital systems do have costs. But their faster speeds and improved accuracy are better value for money. And in the long term or as your company grows, they’ll prove much more scalable.
Efficiency
Your compliance and legal teams are valuable resources. Removing some of the manual, day-to-day tasks they might usually have to complete will help drive their efficiency. They’ll have more time to dedicate to high-priority or time-consuming matters. In their Total Economic Impact Report™ of Onfido, Forrester found that Onfido reduced time manually reviewing verifications by 30%, contributing to an overall ROI of 261%.
Improve the KYC verification process with Onfido
KYC is complex, but the right software solutions make it much simpler. Enter Onfido’s Real Identity Platform: a tool that automates much of the KYC process in a way that’s easier on both the customer and the organization. Additionally, Onfido stays up to date with KYC regulations worldwide, which means no matter where in the world your organization exists, our platform will help you stay compliant — with identity verification, global compliance, fraud prevention, and more.
The Real Identity Platform features a comprehensive suite of verification solutions and fraud detection signals. Take our interactive tour to explore the platform, and walk through how to build KYC workflows in our drag-and-drop orchestration solution, Onfido Studio.